Employee turnover is a simple but powerful HR metric: when left unattended, it can destroy a company’s structure, undermine business performance and eliminate employee morale. At the same time, not every type of employee turnover is negative. Or, wait, you’ve never heard of the 6 types of employee turnover before?
In this article, we’ll learn what employee turnover is, how to calculate it and what is a good employee turnover rate for your business. We’ll also review different types of employee turnover, learn how and why you need to calculate them.
What Is Employee Turnover?
Employee turnover is one of the most important HR metrics reflecting a number of employees who voluntarily or involuntarily leave a company over a certain period of time. Employee turnover can happen for different reasons, including changing jobs or careers, resignation, layoffs, relocation and retirement.
It’s important to measure employee turnover rate because it represents the percentage of employees the company loses on a periodic basis and allows HR teams to examine the reasons for undesirable departures. More than that, employee turnover rate can help you estimate your cost-to-hire for budget projections, training requirements and staff time devoted to recruitment activities.
Employee turnover vs. employee attrition
When defining employee turnover, it’s also important to understand how it’s different from employee attrition, because attrition constitutes a part of the turnover analysis and is sometimes confused with turnover. Here’s a comparison table to help you grasp the difference.
Turnover and attrition are both lagging indicators, meaning the damage has already been done by the time they’re measured. However, both metrics are important.
How to Calculate Employee Turnover?
The basic formula for turnover rate percentage is the number of separations divided by the average number of employees.
Employee turnover rate = (number of separations during a specific time period / average number of employees during the same time period) x 100%
The average number of employees is calculated in the following way:
Average number of employees = (employees at the beginning of the period + the number of employees at the end of the period) / 2
Important: Separations include employees who quit, retired, were dismissed or transferred to another company. They don’t include employees who were promoted or transferred to another department.
Example: Let’s say you had 50 employees at the beginning of the year, 40 employees at the end of the year, and 5 separations. The average number of employees is 45 and the turnover rate is 11%.
This employee turnover rate formula can be modified according to the type of employee turnover you need to calculate. Let’s see what are the types of employee turnover and why they are important.
Types of Employee Turnover
There are two main types of employee turnover: voluntary and involuntary. Voluntary turnover falls into two more types - functional and dysfunctional. And, finally, dysfunctional employee turnover falls into avoidable and unavoidable turnover. Let’s see what these types of employee turnover refer to and why they are important.
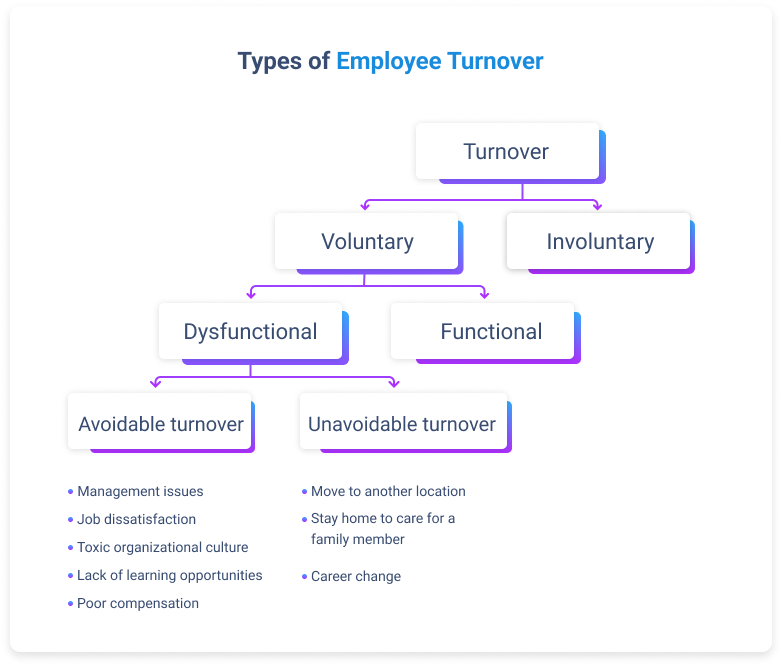
Voluntary employee turnover
Voluntary employee turnover refers to employee departures when people leave the company of their own volition, whether that’s because they got another job elsewhere, took an internal transfer or retired.
Main causes of voluntary employee turnover:
- Career progression
- Management issues
- Job dissatisfaction
- Toxic organizational culture
- Lack of flexibility
- Lack of learning opportunities
- Poor compensation
- Fatigue / exhaustion
How to calculate voluntary employee turnover:

Voluntary employee turnover is typically very expensive to businesses because the cost of re-hiring, onboarding and training is very high and because it often involves the loss of high-performing employees. At the same time, it’s not always an entirely bad thing because it creates opportunities for other talent and fresh ideas.
If voluntary employee turnover is high, use exit interviews to determine causes making employees leave the organization.
Involuntary employee turnover
Involuntary employee turnover refers to cases when an employer chooses to terminate an employee.
Main causes of voluntary employee turnover:
- Poor performance
- Violation of company policy
- Unsatisfactory performance within probationary period
- Reduction in workforce
How to calculate involuntary employee turnover:

If you have high involuntary employee turnover, start by seeing if there is a common department or manager first and investigate the reasons behind their decisions. Use the results of exit interviews when developing a solution with executives.
Functional employee turnover
Functional employee turnover is a type of voluntary employee turnover that includes cases of low-performing employees leaving the organization.
Functional turnover is a positive example of employee turnover because these separations will have minimal impact on business productivity and employee morale (compared to termination cases). With this type of employee turnover, the benefits gained by hiring a replacement exceed the costs incurred.
Dysfunctional employee turnover
Dysfunctional employee turnover involves the separation of employees who are highly skilled and productive.
Dysfunctional turnover hurts the company because it loses top performers who had a direct impact on profitability because they possessed unique knowledge and skills. Costs associated with finding a replacement or training other employees will exceed any potential benefits.
Unavoidable employee turnover
Unavoidable employee turnover involves cases when employees leave the company due to the reasons over which the company has no control. These include family and health issues and moving to a new location,
Avoidable employee turnover
Avoidable turnover is when the company does have control over the reasons for employee separations. In other words, those employees could continue to generate profit for the business but became so dissatisfied with their job, so they quit. This type of employee turnover is important and requires detailed investigation.
What Is a Good Employee Turnover Rate
Turnover rates vary widely from industry to industry. The following diagram displays the annual turnover averages across industries in the US that range from 15% to 31%.
While it’s hard to determine a universal benchmark, there’s a general recommendation that companies should aim for anything between 12% and 20%. Turnover rates of more than 20% should be investigated, unless they refer to industries with higher employee turnover rates due to the nature of the job such as retail, staffing agencies, hospitality and fast food.
Why Employee Turnover Matters?
Employee turnover is one of the most important HR metrics to measure in every company. Different types of employee turnover allow you to hone in on trends for certain types of departures: voluntary turnover rate displays how many employees left the organization voluntarily and it’s a great tool to review their exit interview points and look into the reasons.
Calculating turnover rate on a monthly, quarterly or annual basis is important to compare previous metrics and think of the reasons why the metric has changed and what it teaches you. Training and recruiting are expensive for businesses in terms of time and cost, but as an HR manager you can introduce change by tracking and comparing a single HR metric.
Ready to Reduce and Prevent Employee Turnover?
One of the important indicators that an employee struggles with their job or is planning to leave is attendance issues. These include tardiness, absenteeism, frequent sick leaves and absence patterns. So one of the most effective tips on how to prevent employee departures and keep employee turnover to the minimum is to keep track of employee attendance and absences.
Leave management software most often constitutes a part of expensive HR suites, but not actiPLANS. It is a team calendar where employees can register their absences, work statuses, running late or leaving early cases. Automated leave balances allow employees to review their PTO and sick leave balances while the online team calendar and the mobile app allow them to request a leave in a few clicks.
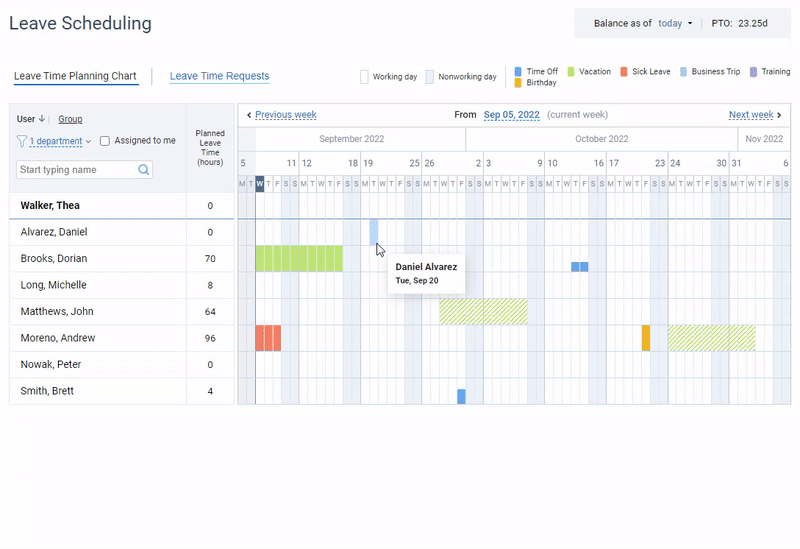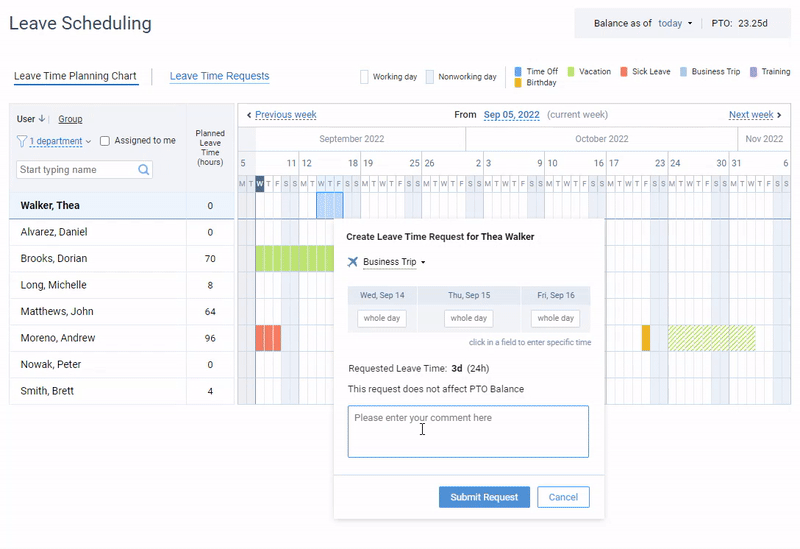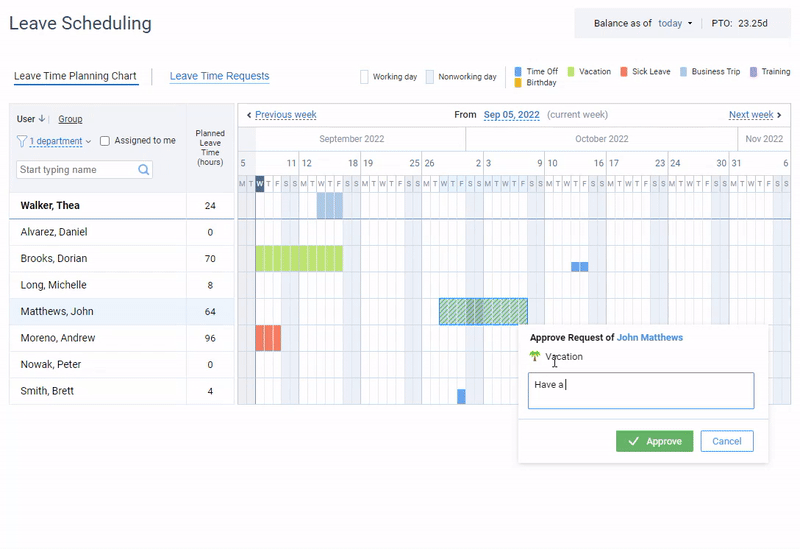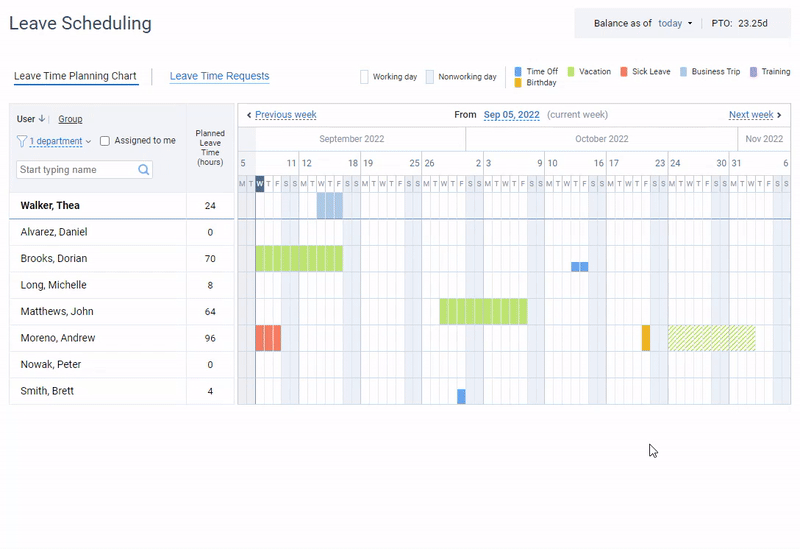
Leave management in actiPLANS – create an unlimited number of leave types, get your team to request and plan their time off and review employee availability
actiPLANS subscription starts at $1.5 per user per month making it an absolute leader on the market. More than that, you can use it for free for 30 days to explore the software and see if it fits your company. Get your free 30-day actiPLANS trial now (no credit card required).



